Grape variety
A grape variety is a type of vine plant characterised by the skin, size and constitution of its berries and by its foliage. Most often belonging to the Vitis vinifera species of vine, it can be either a table grape or a wine grape, used to make wine.
What is a grape variety in the wine world?
Chardonnay, Gamay, Gewurztraminer, Muscat, Savagnin... There are more than 6,000 of them in the world!
Red or white, what does the definition of a grape variety actually mean in oenology? Originally, it referred to a type of vine plant in its entirety, from roots to bunches. But in the 19th century, the devastation of European vineyards by phylloxera (an aphid) led winegrowers to import American vines resistant to this insect. They were then used as rootstocks for cuttings of the "surviving" European grape variety. As the practice of grafting has become more widespread throughout the world, the notion of grape variety, or "cultivar" in viticulture, now refers to a grafted vine plant. It therefore refers to the graft and, by extension, to the fruit, stalks and leaves of the plant.

Aveine's Precision
A grape variety can come in several varieties: for pinot, there's pinot noir, pinot gris and pinot blanc!
Oenology: how to recognise a grape variety?
This is the challenge of ampelography, the study of grape varieties, whose organoleptic expression depends on the vineyard, and therefore the terroir.
| Characteristics of a grape variety | Details |
|---|---|
| Skin colour | From yellow-green to purplish red. Defines a red or white grape variety |
| Skin thickness | Impacts its aromas as well as its tannin and pigment content |
| Leaves | Colour and shape of leaves |
| Berry size | Large (table grapes) / Medium (table grapes and wine grapes)/ Small (wine grapes) |
| Chemical composition of the grapes | Influences the aromas, acidity and tannins of a wine |
| Characteristics of a grape variety | Skin colour |
| Details | From yellow-green to purplish red. Defines a red or white grape variety |
| Characteristics of a grape variety | Skin thickness |
| Details | Impacts its aromas as well as its tannin and pigment content |
| Characteristics of a grape variety | Leaves |
| Details | Colour and shape of leaves |
| Characteristics of a grape variety | Berry size |
| Details | Large (table grapes) / Medium (table grapes and wine grapes)/ Small (wine grapes) |
| Characteristics of a grape variety | Chemical composition of the grapes |
| Details | Influences the aromas, acidity and tannins of a wine |

Aveine's Advice
The key to recognising a grape variety when tasting?To combine sensory expertise with a sound theoretical knowledge of the characteristics of grape varieties and terroirs!
Are grape variety and wine name the same thing?
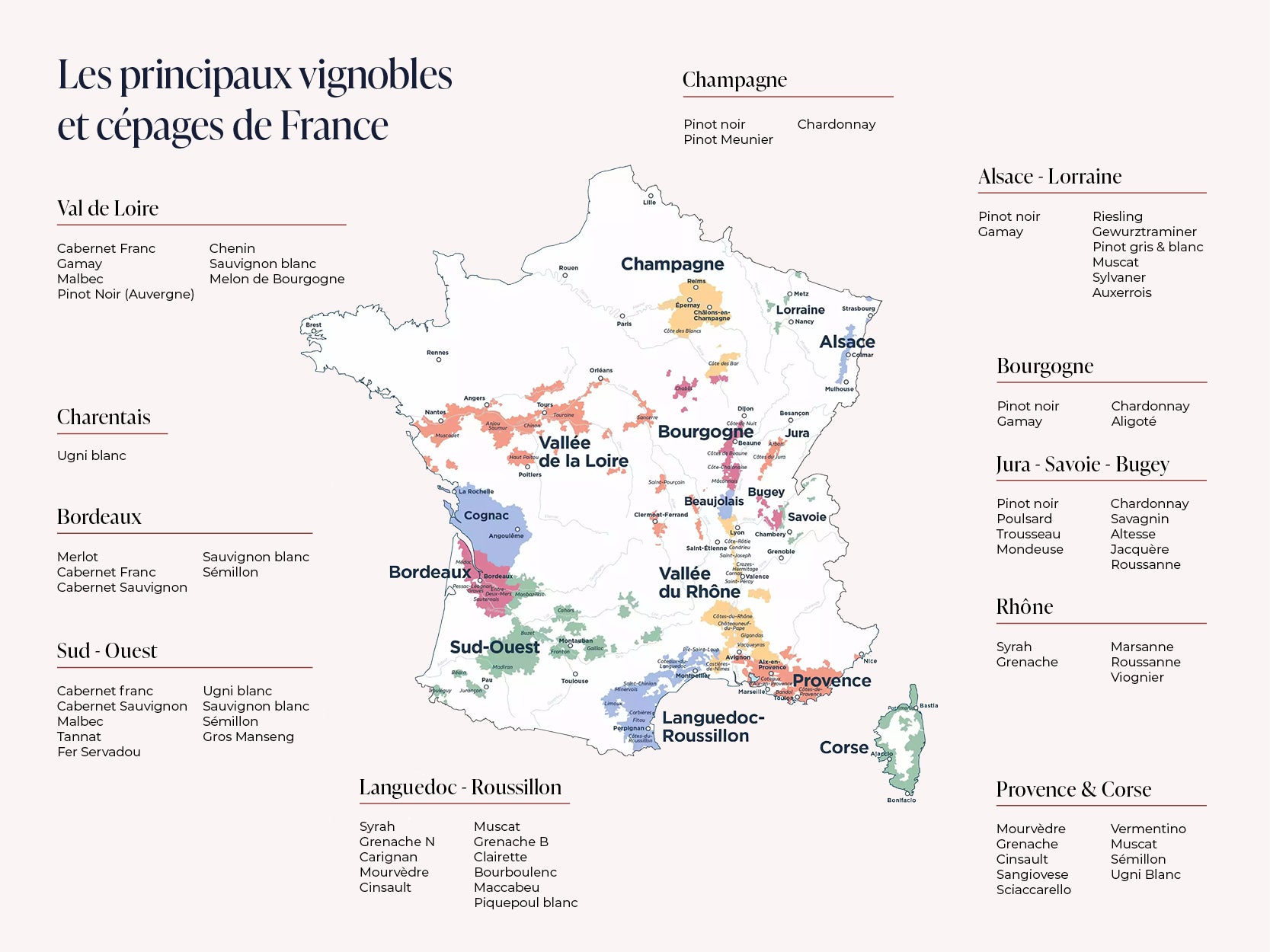
In most countries, wines are named according to the grape varieties they are made from. In France, the name of a wine refers to the terroir and therefore the region: wine from Bordeaux, Burgundy, Languedoc, the Rhône Valley, the South-West, the Loire Valley, Savoy, the Jura, a rosé from Provence, and so on. In the case of AOP wines (Bordeaux, Burgundy, Champagne, etc.), their production is even strictly controlled by a specification detailing the authorised grape varieties. A precise blend of Merlot, Cabernet Sauvignon and Cabernet Franc is referred to as "Bordeaux".

Aveine's Precision
Unlike a single-varietal wine, a blend is a wine made from several complementary grape varieties.
Which grape varieties are grown most often?
Grape varieties - the varieties grown in a given geographical area - vary from region to region, country to country and continent to continent.
List of the most widely grown grape varieties in France, by number of hectares under vine
- 1 – Merlot
- 2 – Ugni blanc
- 3 – Grenache noir
- 4 – Syrah
- 5 – Chardonnay
- 6 – Cabernet sauvignon
- 7 – Cabernet franc
- 8 – Carignan
- 9 – Pinot noir
- 10 – Sauvignon blanc
List of the most widely grown grape varieties in the world, by number of hectares under vine
- 1 – Cabernet sauvignon
- 2 – Merlot
- 3 – Airen
- 4 – Tempranillo
- 5 – Chardonnay
- 6 – Syrah
- 7 – Grenache noir
- 8 – Sauvignon
- 9 – Pinot noir
- 10 – Ugni blanc
And what about old vines?
Despite their renown, these international grape varieties remain vulnerable to certain diseases and global warming. Older, more resistant varieties are therefore being reintroduced in many vineyards.